What Does It Mean to Upload Something?
In the context of the web, upload
= send. You can think of it like loading the data "upward" to the
cloud/internet.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/cloud-upload-a30f385a928e44e199a62210d578375a.jpg)
When you upload something to a
website, another user's computer, a network location, etc., you're sending data
from your device to the other device. Files can be uploaded to a server, such
as a website, or directly to another device, like when using a file transfer
utility.
For example, if you upload an
image to Facebook, you're sending the picture from your device to the Facebook
website. The file started with you and ended up somewhere else, so it's
considered an upload from your perspective.
This is true for any transfer
like this, no matter the file type or where it's going. You can upload
documents to your teacher via email, upload a video to YouTube, upload music to
your online music collection, etc.
What does download speed mean?
In opposition to upload, download
= save. You're taking data from elsewhere and putting it onto your device,
essentially bringing it "down" from the internet.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/download-7105085d68424c93a47bcc6228d946fa.png)
What does download speed mean
that you're transferring data from the other location to your own device,
whether it be your phone, computer, tablet, smartwatch, etc.
All sorts of information can be
downloaded from the web: books, movies, software, etc. For example, you can
download movies to your phone to watch while you're on the go, which means that
the actual data that makes up the movie is transferred from the site you got it
from and saved to your phone, making it locally available.
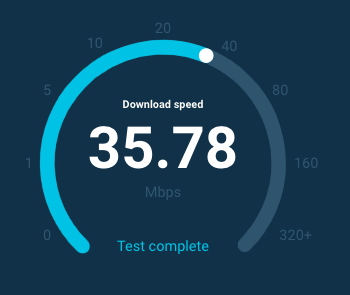
What does download and upload speed mean, when I do a speed test of my internet connection?
What does download and uploadspeed mean? is how fast you can pull data from the server to you. Cable
companies set the default setting to download faster than upload. The reasoning
behind this is that most people have more of a need to download information. It
gives the user the ability to download movies, songs, or stream videos.

Both download speed and upload
speed are measured in megabits per second (Mbps)
You've probably heard the terms
"upload" and "download" many times, but what do these terms
actually mean? What does upload and download speed mean? What does it mean to
upload a file to a website or download something from the web? What's the
difference between a download and an upload?
These are basic terms that any
web user should understand. They come into play when following some directions,
troubleshooting network issues, choosing your internet speed, and more.
Below, we'll go over what is
download speed vs upload speed, as well as common peripheral terms and
information that will help you have a firmer grasp of these common online
processes.
Upload vs. Download: How They Relate
Considering that an upload is
sending data, and a download is saving data, you might have caught on already
that this goes on all the time when you use the web.
Open your web browser and go to
Google.com, and you immediately requested the site (uploading tiny bits of data
in the process) and got the search engine in return (it downloaded the correct
web page to your browser).
Here's another example: when you
browse YouTube for music videos, each search term you enter is sending tiny bits
of data to the site to request the video you're looking for. Each of those
requests you send are uploads since they started on your device and ended up on
YouTube's end. When the results are understood by YouTube and sent back to you
as web pages, those pages are being downloaded to your device for you to see.
For a more concrete example,
think about an email. You're uploading the pictures to an email server when you
send someone photos over an email. If you save picture attachments from someone
who sent you an email, you're downloading them to your device. Another way to
see it: you upload the images so that the recipient can view them, and when
they save them, they're downloading them.
It's Important to Know the Difference
what are download and upload
speeds happen all the time in the background? You don't usually need to
understand when something is uploading or downloading or what they really refer
to, but knowing how they differ is important in some situations.
For example, if a website tells
you to upload your resume using their online form, but you don't know if that
means to save something to your computer or send them a file, it can get
confusing and delay the overall process you're trying hard to finish.
Or, maybe you're buying a home
internet plan and you see one advertised as offering 50 Mbps download speeds
and another with 20 Mbps upload speeds. Most people don't need a fast upload
speed unless they're often sending large amounts of data over the internet. However,
not knowing the difference between what do upload and download speeds mean
might leave you paying for way more than you need, or paying a smaller amount
for speeds too slow for what you need.
What About Streaming?
Since the speed at which you can
download things from the internet is determined by what you're paying your ISP
for, some people opt to stream data versus download it. They're similar, but not
technically the same, and there are benefits of both.
For example, there are movie
streaming sites that let you watch movies online instead of downloading them, and
web apps that can be used in a browser instead of saved to your device.
Downloading is useful if you want
the entire file for offline use like if you plan to watch movies, edit
documents, view photos, or listen to music without an internet connection. The
entire file is saved on your device since you downloaded it, but to use it, you
have to wait for the whole download to finish.
Streaming, on the other hand, is
useful if you want to use the file before it's finished downloading. You can
stream Netflix shows on your tablet without needing to download the whole
episode first. However, the file isn't usable offline because it isn't stored
for future use.
Other Facts About Uploading and Downloading
what is upload and download speed
mean are usually reserved for transfers that take place between a local device
and something else on the internet? For example, you won't say that you've
"uploaded data to your flash drive" when copying a file to it from
your computer.
There are network protocols that
support data uploads and downloads. One is FTP, which utilizes FTP servers and
clients to send and receive data between devices. Another is HTTP, which is the
protocol used when you upload/download data through your web browser.
Comments
Post a Comment